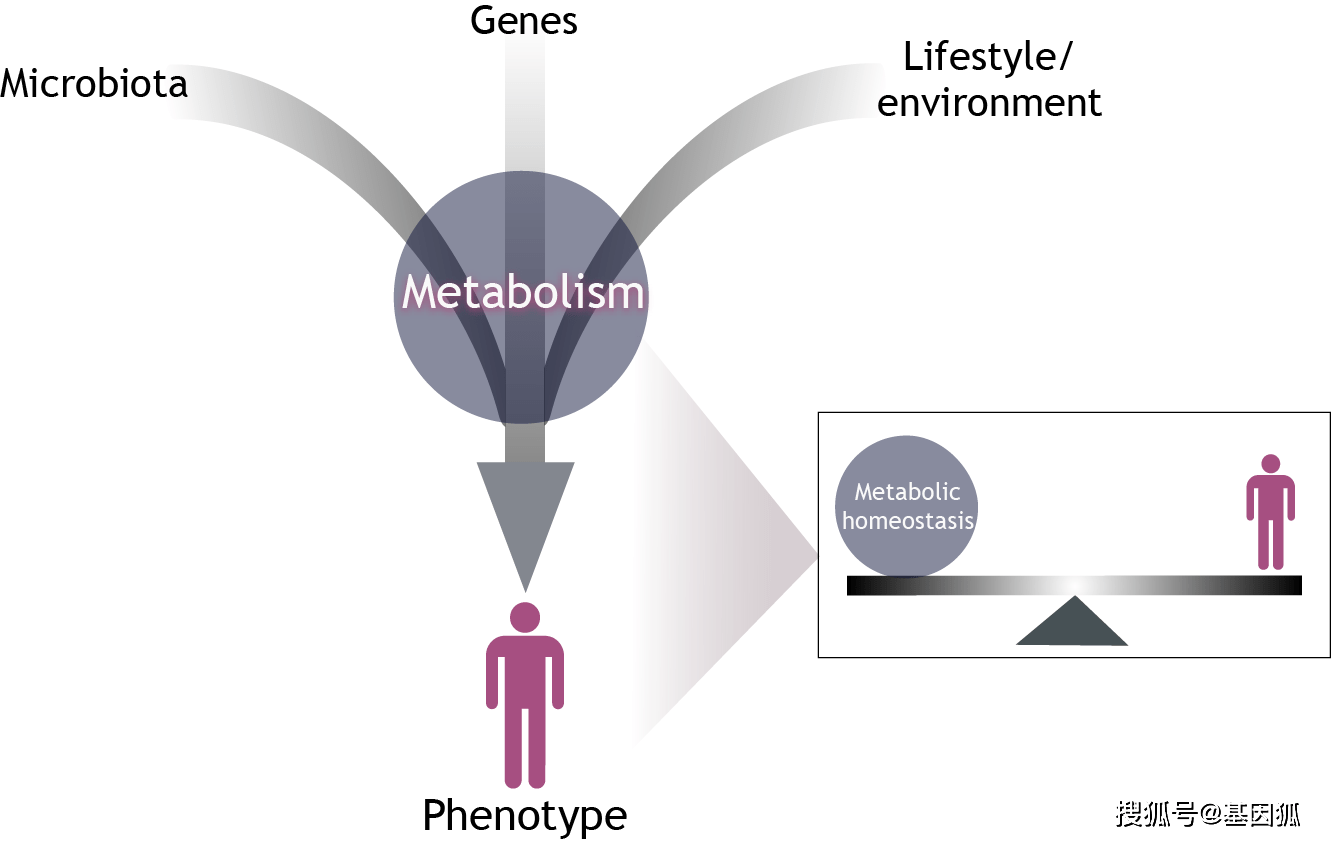
代谢组学(Metabonomics/Metabolomics)是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新兴发展起来的学科,是生命科学研究的必然。 在20世纪90年代中期发展起来的代谢组学,是对某一生物或细胞中相对分子量小于1,000的小分子 代谢产物进行定性和定量分析的一门新学科。代谢组反应营养、胁迫或者疾病状态的速度比转录组或者蛋白质组要快得多。这使得代谢组在许多领域都非常吃香,如环境毒理学、进化和发育、疾病诊断与治疗反馈、以及药物、杀虫剂和除草剂的研发等。代谢组流动检测帮助合成生物学家揭示遗传改变如何影响通路和产物。
 图片来自:outsourcedpharma
图片来自:outsourcedpharma
代谢全谱分析采用液相色谱-质谱联用采集样品的代谢物质谱图,比较不同组样品代谢产物的含量,寻找差异代谢物,并探索差异代谢物之间的代谢通路。代谢组学对内源性代谢物进行前景的定性和定量分析,找出差异代谢物,用于药物靶点发现、疾病机理研究等。其分析策略主要有非靶向和靶向两种,前者信息丰富,但存在数据复杂、重复性差、线性范围窄等缺点;后者数据质量好,但通常只能检测已知代谢物,覆盖度低。
 靶向代谢组学技术路线
靶向代谢组学技术路线
针对上述问题,研究团队于2012年首次提出拟靶向代谢组学的概念,将非靶向和靶向代谢组学检测方法“强强结合”,使得已知和未知的代谢物均可被测量,兼具非靶向和靶向代谢组学方法的优点。
 论文截图
论文截图
研究人员不断对该方法进行完善和提升,开发了大量相关软件,建立了针对大规模临床样本分析的数据校正方法,获得了很好的重复性。在此基础上,在不同色谱—质谱检测体系中分别建立了对血浆、尿液、植物样品等的拟靶向代谢组学和脂质组学方法。
 拟靶向代谢组学检测方法技术路线
拟靶向代谢组学检测方法技术路线
近期团队应用二维液相色谱—质谱技术在正离子模式和负离子模式下分别检测到1294和687个离子对,分别对应1609和847个潜在代谢物或脂质。而基于化学标准品的传统靶向方法,通常只能检测几十到几百个代谢物或脂质。新方法可用于分离分析氨基酸、胆汁酸、肉碱等,已在恶性肿瘤(肝癌、肺癌)和糖尿病等代谢性疾病的研究中发挥积极作用。
团队还进一步优化了拟靶向代谢组学检测方法建立流程,升级了开放式软件和工具,形成了方法范本,为领域内同行更好地利用该方法提供理论和操作指南,相关研究相关成果发表于成果《Nature Protocols》上。
Abstract
Untargeted methods are typically used in the detection and discovery of small organic compounds in metabolomics research, and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) is one of the most commonly used platforms for untargeted metabolomics. Although they are non-biased and have high coverage, untargeted approaches suffer from unsatisfying repeatability and a requirement for complex data processing. Targeted metabolomics based on triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry (TQMS) could be a complementary tool because of its high sensitivity, high specificity and excellent quantification ability. However, it is usually applicable to known compounds: compounds whose identities are known and/or are expected to be present in the analyzed samples. Pseudotargeted metabolomics merges the advantages of untargeted and targeted metabolomics and can act as an alternative to the untargeted method. Here, we describe a detailed protocol of pseudotargeted metabolomics using UHPLC-TQMS. An in-depth, untargeted metabolomics experiment involving multiple UHPLC-HRMS runs with MS at different collision energies (both positive and negative) is performed using a mixture obtained using small amounts of the analyzed samples. XCMS, CAMERA and Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM)-Ion Pair Finder are used to find and annotate peaks and choose transitions that will be used to analyze the real samples. A set of internal standards is used to correct for variations in retention time. High coverage and high-performance quantitative analysis can be realized. The entire protocol takes ~5 d to complete and enables the simultaneously semiquantitative analysis of 800–1,300 metabolites.
参考文献
Zheng, F., Zhao, X., Zeng, Z., Wang, L., Lv, W., Wang, Q., & Xu, G. (2020). Development of a plasma pseudotargeted metabolomics method based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols.
- 本文固定链接: https://oversea.maimengkong.com/zu/1728.html
- 转载请注明: : 萌小白 2024年5月3日 于 卖萌控的博客 发表
- 百度已收录
