2021年第39周。
这一周R语言学习,记录如下。
01
Modern Statistics with R
一本在线开放书籍,介绍R语言做数据整理和探索,以及推断和预测的工作。

访问网址:
http://www.modernstatisticswithr.com/
02
R4DS书籍
最近,我在重温R4DS这本书籍。

你所想的数据科学是什么?
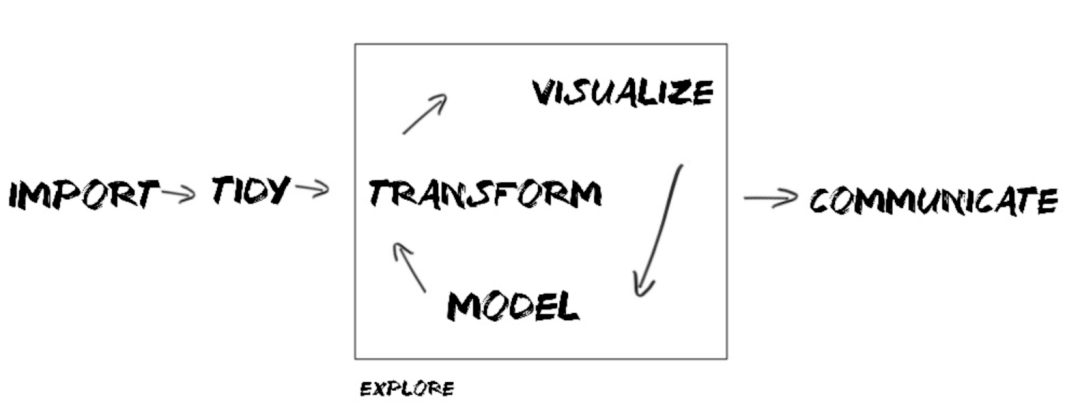
实际中的数据科学是什么?
数据的准备工作,需要花费大部分时间。
我创建了R4DS学习群,加我的微信,备注:R4DS,邀请你入群,大家一起学习,同时,也会分享R4DS相关的资料。
03
dplyr包的join系列函数
数据关联是数据集成和整合的常用操作。
dplyr包提供了一组功能强大的join函数集,可以方便地实现数据的关联。
1 inner_join函数

2 left_join函数

3 right_join函数
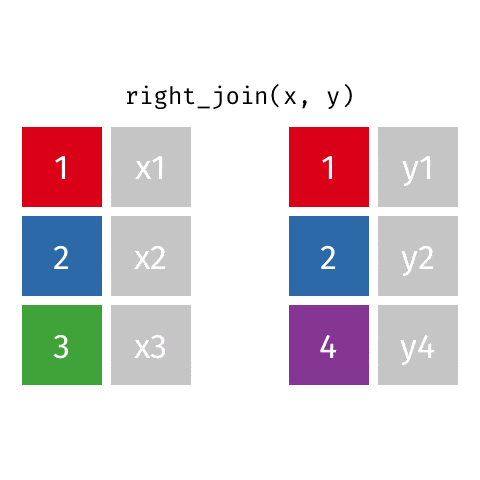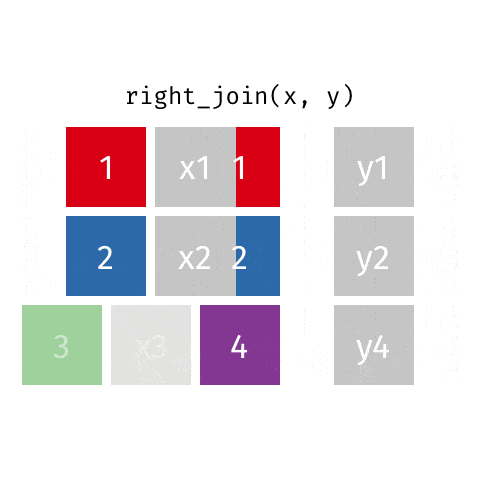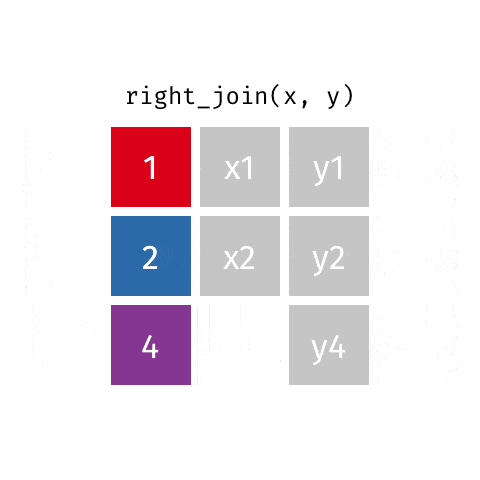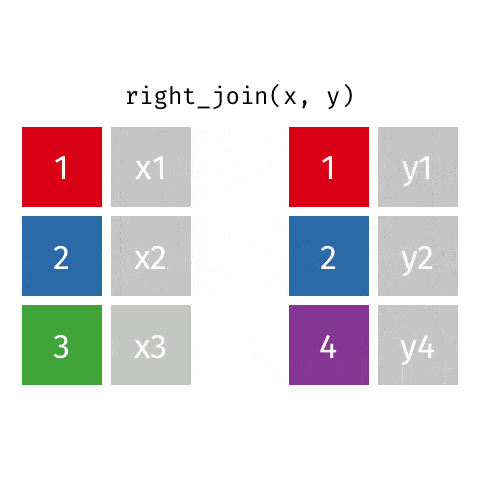
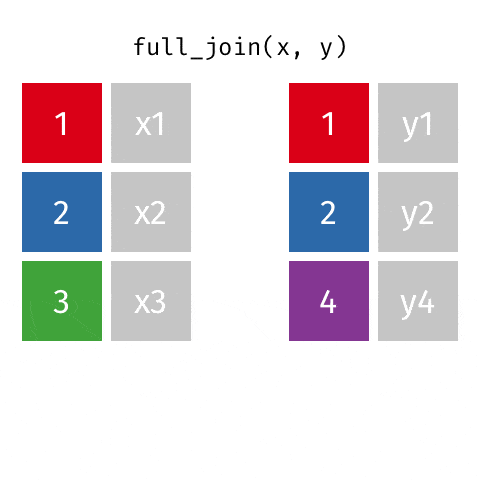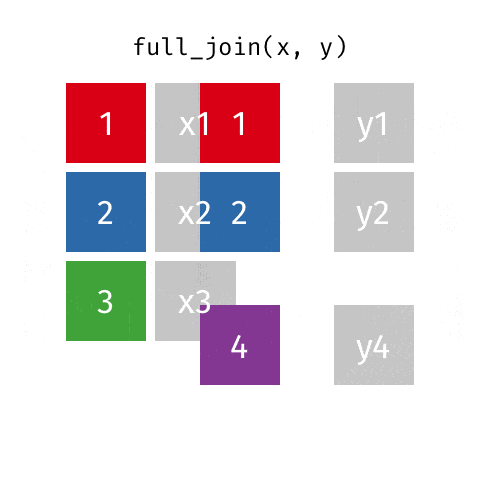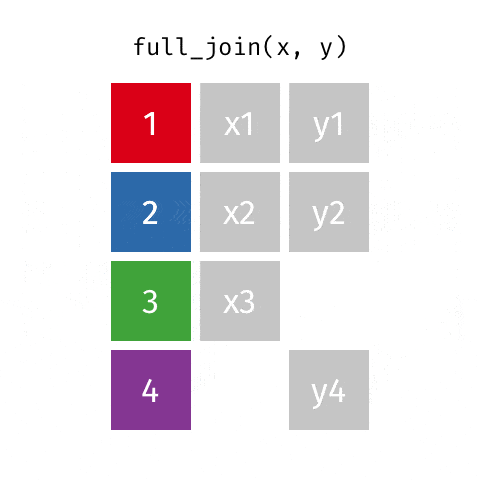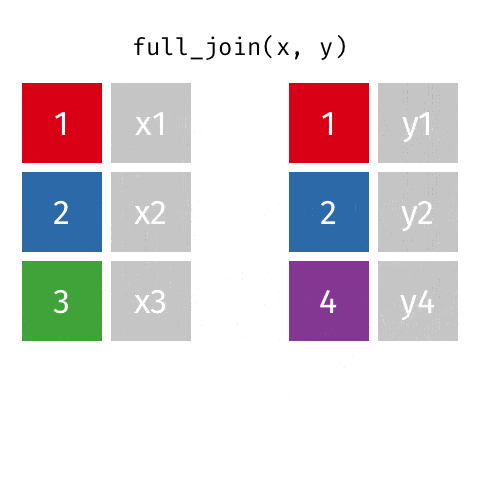
4 full_join函数
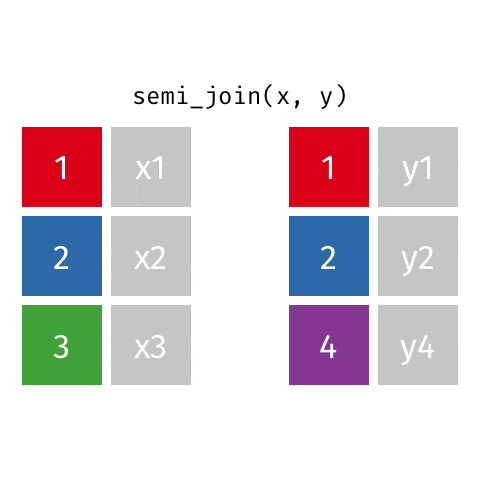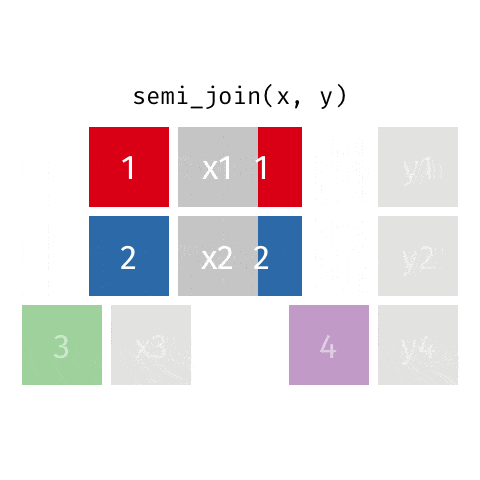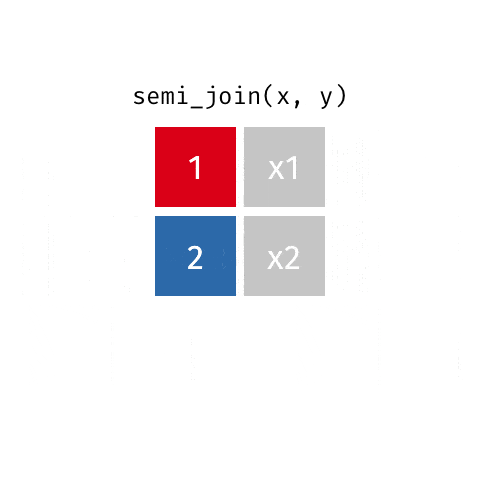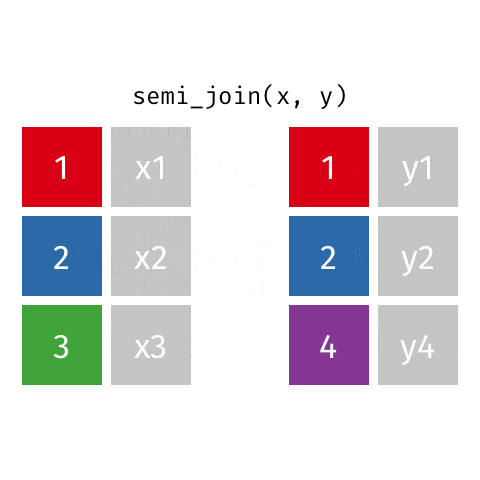
5 semi_join函数
6 anti_join函数
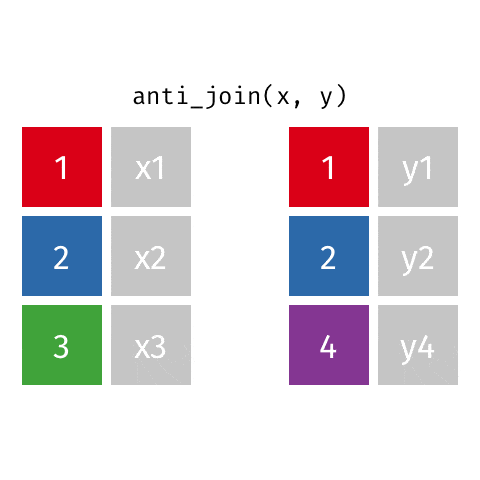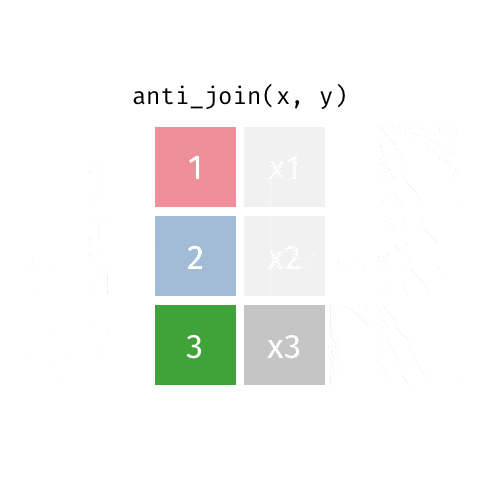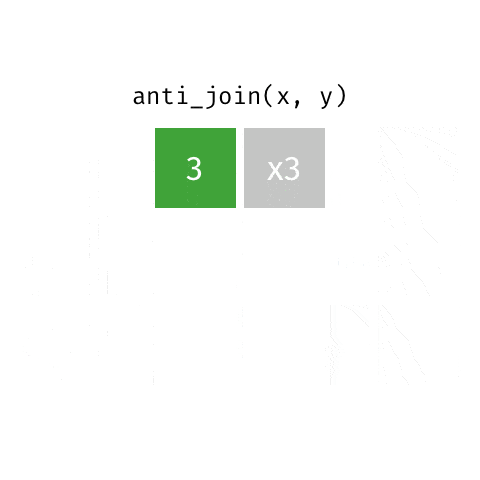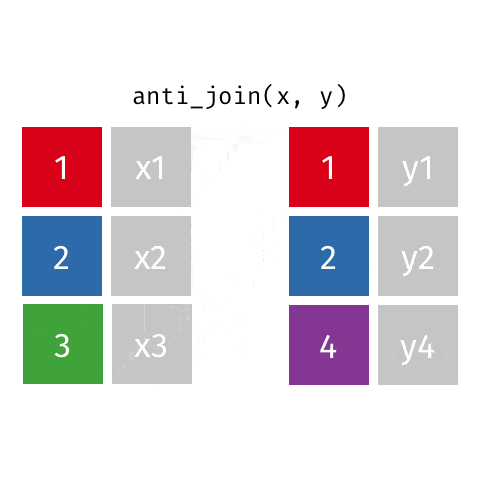
关于这6种join操作,你理解了吗?有任何问题或者想法,请加入R4DS学习群,一起讨论。
04
样本选择
dplyr包的filter函数提供了强大的样本选择功能。
filter函数理解。

05
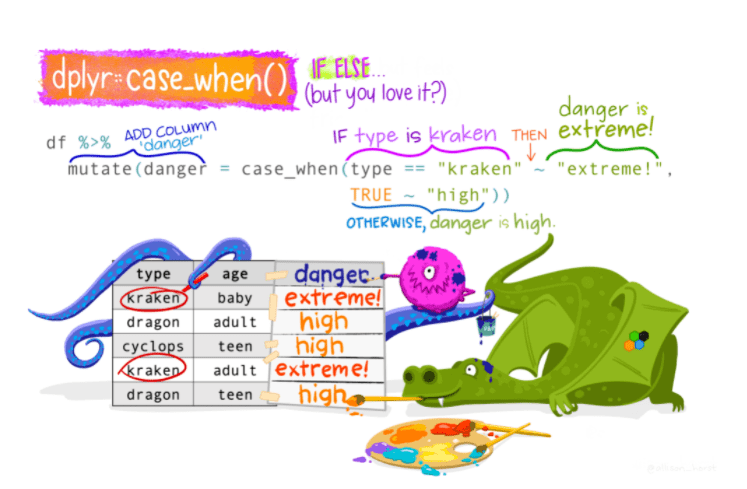
case_when函数理解
dplyr包的case_when函数实现开关选择操作。
case_when函数理解。
06
R4DS第一章 ggplot2包与数据可视化简要笔记
1 为什么需要数据可视化?

2 ggplot2包做数据可视化的逻辑
图形语法+分层架构

3 内容结构
1)准备工作
2)以研究mpg数据displ与hwy的关系的问题做引子,介绍利用数据可视化技术做图形化分析
3)接下来介绍ggplot画图的重要组件
Aesthetic Mapping
Facets
Geometric Objects
Statistical Transformations
Position Adjustments
Coordinate Systems
4) 图形学的分层语法

4 目标管理
1)理解ggplot2包画图的基本逻辑和原理。
2)掌握常用的5种图形,散点图、条形图、盒箱图、直方图、点线图。
3)学会用图形化思维对数据做探索、理解和表达。
5 实操代码
graphics.off()
rm(list = ls())
options(warn = -1)
options(scipen = 999)
options(digits = 3)
# R4DS第一章 ggplot2包与数据可视化
# 准备工作
library(tidyverse)
# 数据可视化的流程
# 提问题--找数据--选图形--做图形--得信息--导行动
# 例如:想了解引擎尺寸和燃油效率的关系?
# 正向还是负向;线性还是非线性?
# 使用自带的mpg数据库
data(mpg)
mpg %>% glimpse()
mpg %>% head
help(mpg)
# 找到数据集,需要寻找或者构建与问题相关的变量或者特征
# 1)displ 引擎的尺寸
# 2)hwy 燃油效率 每加仑油对应的行驶距离 相同距离下,高效率相对于低效率需要更少的油
# 绘制图形
# 探索两个变量之间的关系
# 变量数目: 2个
# 变量类型:连续型
# 采用散点图
# 根据变量的类型和数目,选择合适的图形
# 坐标轴 x--displ y--hwy
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = displ, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = 'lm', se = FALSE)
ggplot( data= mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = 'lm', se = FALSE) +
theme_classic()
# 必要三组件
# 1)数据集
# 2)几何图形对象
# 3)映射关系,变量映射到坐标轴、尺寸、颜色、透明度等
# 通用模板
# ggplot( data= <DATA>) +
# <GEOM_FUNCTION>(mapping = aes(<MAPPING>))
# 练习 1
ggplot( data= mpg)
mpg %>% glimpse()
?mpg
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = cyl, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = drv, y = class))
# 思考:
# 一幅简洁的图能够带来什么信息?
# 差异化标识
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = displ, y = hwy, color = class))
# 分面板观察
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_wrap(~ class, nrow = 2)
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_grid(drv ~ cyl)
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_grid(. ~ cyl)
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_grid(drv ~ .)
# 不同的画图几何对象
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy, linetype = drv))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x =displ, y = hwy, color = drv)) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ,
y = hwy,
linetype = drv,
color = drv))
# 添加趋势线
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ,
y = hwy,
group = drv))
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ,
y = hwy,
color = drv),
show.legend = FALSE)
ggplot( data= mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy))
ggplot( data= mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth()
ggplot( data= mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = class)) +
geom_smooth()
ggplot( data= mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = class)) +
geom_smooth(
data= filter(mpg, class== "subcompact"),
se = FALSE
)
# 统计变换
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut))
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
stat_count(mapping = aes(x = cut))
# 参数stat明示化的 3种情况
# 构造数据集
demo <- tribble(
~a, ~b,
"bar_1", 20,
"bar_2", 30,
"bar_3", 40
)
ggplot( data= demo) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = a, y = b),
stat= 'identity'
)
# 绘制每一组的百分比
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = cut, y = ..prop.., group = 1)
)
# 统计图形可视化
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
stat_summary(
mapping = aes(x = cut, y = depth),
fun.min = min,
fun.max = max,
fun= median
)
# 位置调整
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, color = cut))
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = cut))
ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity))
ggplot(
data= diamonds,
mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity)
) +
geom_bar(alpha = 1/ 5, position = 'identity')
ggplot(
data= diamonds,
mapping = aes(x = cut, color = clarity)
) +
geom_bar(fill = NA, position = 'identity')
ggplot(
data= diamonds
) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity),
position = 'fill'
)
ggplot(
data= diamonds
) + geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity),
position = "dodge"
)
ggplot(
data= mpg
) + geom_point(
mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy),
position = "jitter"
)
# 坐标系统
ggplot( data= mpg, mapping = aes(x = class, y = hwy)) +
geom_boxplot()
ggplot( data= mpg, mapping = aes(x = class, y = hwy)) +
geom_boxplot() +
coord_flip()
nz <- map_data( "nz")
ggplot(nz, aes(long, lat, group = group)) +
geom_polygon(fill = "white", color = "black")
ggplot(nz, aes(long, lat, group = group)) +
geom_polygon(fill = "white", color = "black") +
coord_quickmap()
bar <- ggplot( data= diamonds) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = cut),
show.legend = FALSE,
width = 1
) +
theme(aspect.ratio = 1) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)
bar + coord_flip()
bar + coord_polar()
6 部分结果展示(大家可以自测代码)
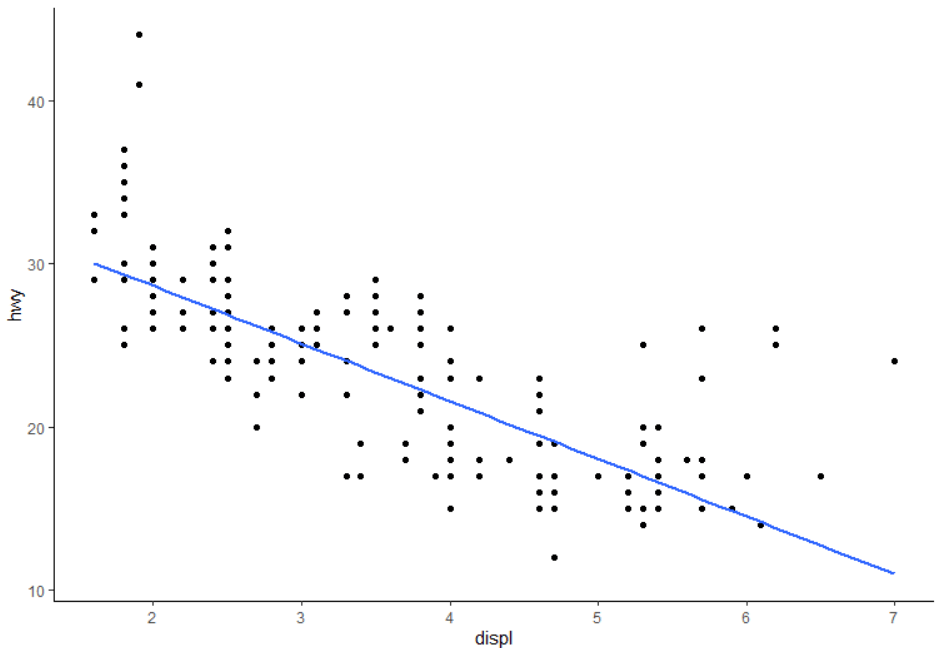


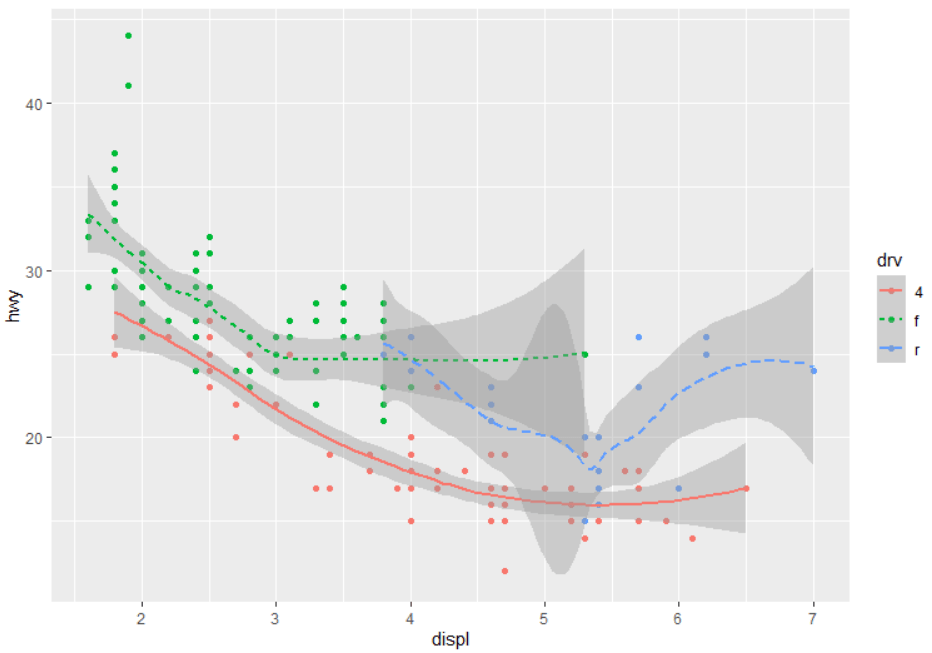
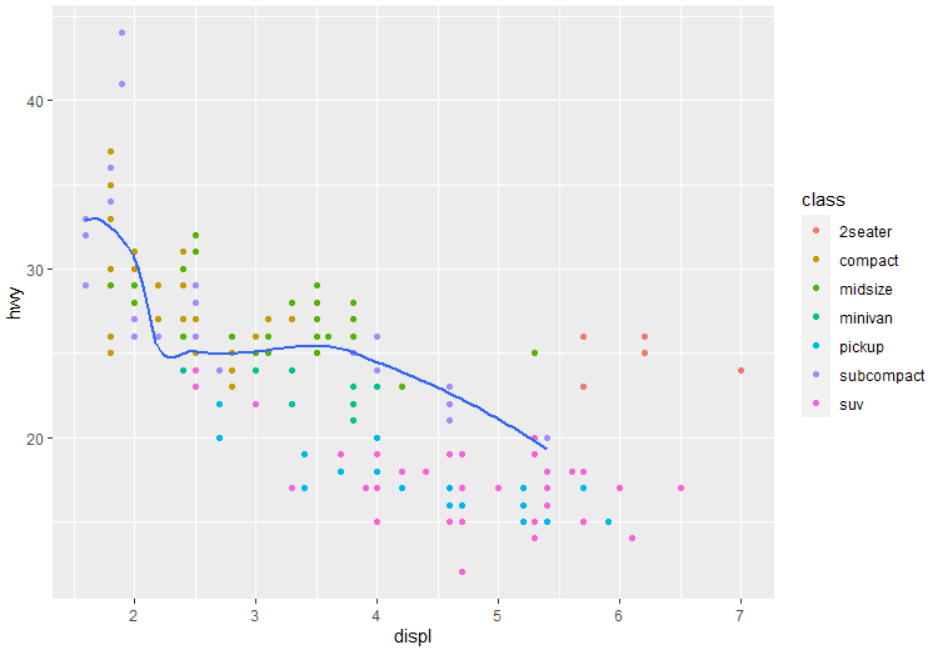

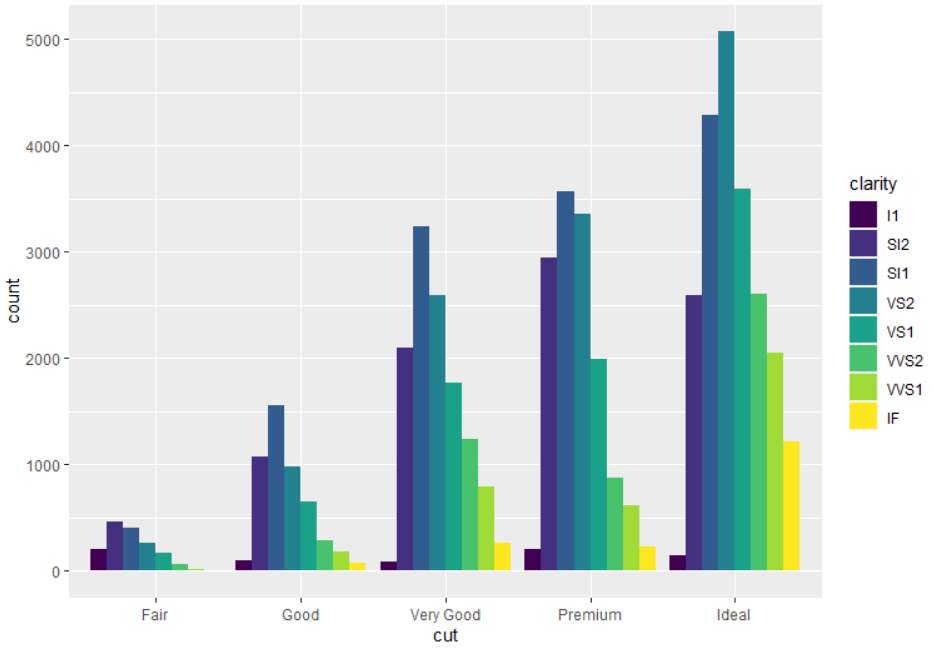
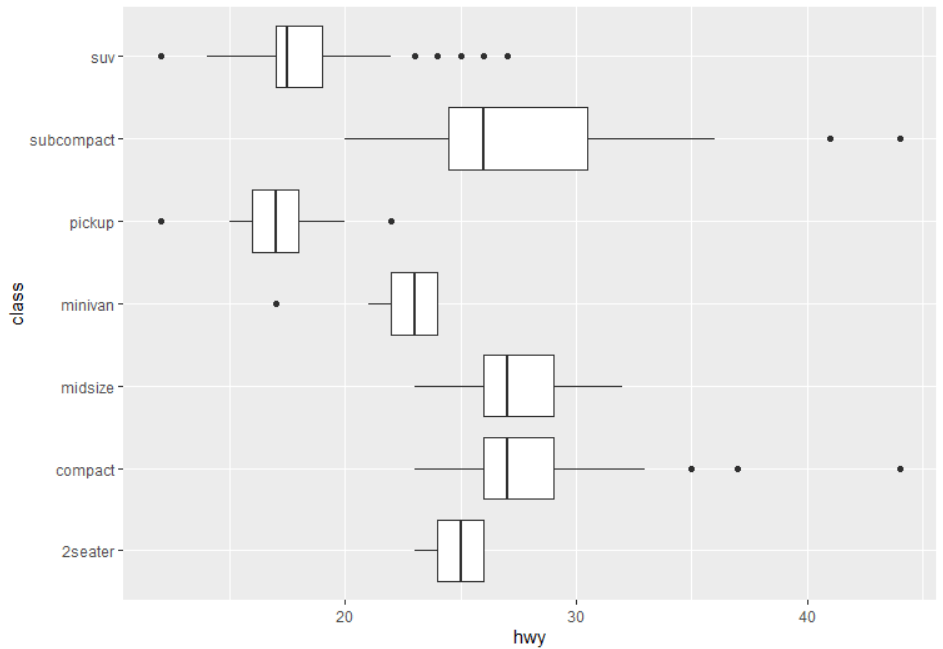

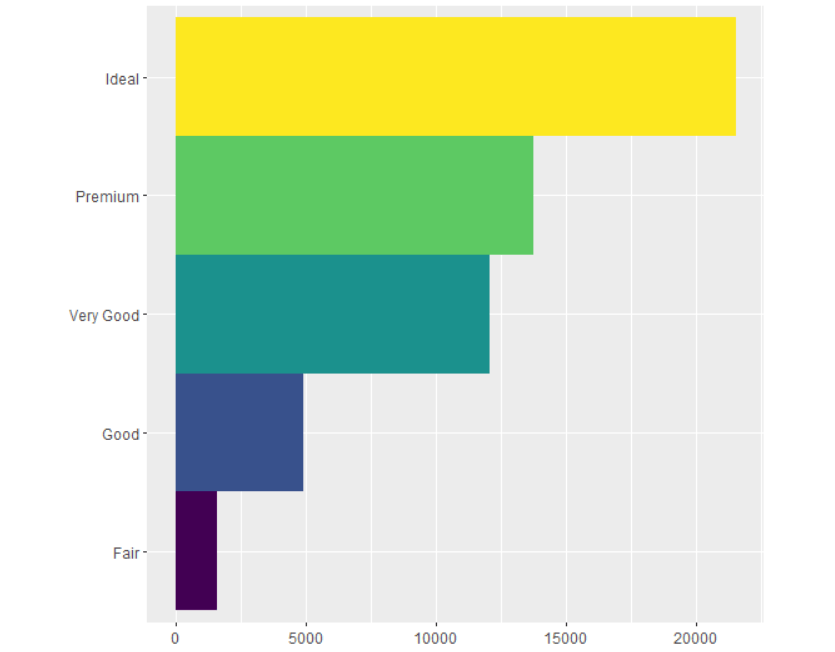

07
可重复性代码构建指南
创建项目工程,做项目管理
项目的层级架构,参考下图:
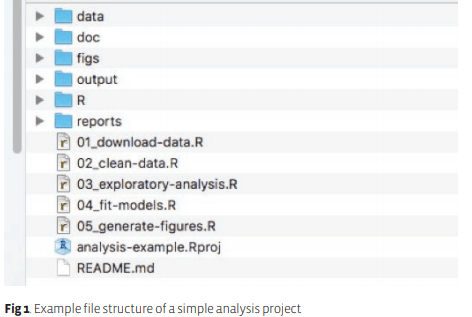
各个文件夹和文件的用途

请注意
1 永远不要修改原始数据,或者说,一定要备份好原始数据
2 对于任何项目,创建一个文件,记录你的所思和所做,便于复盘和迭代
3 脚本的命名,请知名晓意,赋予含义,具有条理性和逻辑性,重视代码的可读性,代码是让电脑来运行的,更重要的是,让人来看的。
4 对于一个复杂的项目,编写代码之前,先写伪代码或者画流程图
08
md5加密
实际工作中,有时候需要抽取内部数据与第三方数据做撞库操作。这个时候,需要把敏感信息,比方说,身份证号码、手机号码、姓名做加密处理,常用md5加密。
digest包的digest函数,可以方便地进行md5加密。
library(diges)
id1 <- "1234567890"
id1
id1_md5 <- digest(id1, algo = "md5", serialize = FALSE)
id1_md5
补充信息
源自:https://github.com/BaHui/MD5Hash
MD5加密是最常用的不可逆加密方法之一,是将字符串通过相应特征生成一段32位的数字字母混合码。对输入信息生成唯一的128位散列值(32个16进制的数字)
但是常见的会有16位和32位长度之分, 实际上MD5产生的就是唯一的32位的长度, 所谓的16位的长度可以理解为对MD5的再加工而形成的. 再加工就是: 32 位字符串中,取中间的第 9 位到第 24 位的部分
09
dplyr包across函数
dplyr包across函数,把一个函数或者一系列函数应用到一些具有某种模式下的列做处理。
# dplyr包across函数
library(dplyr)
library(magrittr)
help( package= 'dplyr')
iris %>%
group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(across(starts_with( "Sepal"), mean), .groups = "drop") %>%
View
iris %>%
group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(across(starts_with( "Sepal"), list(mean = mean, sd = sd)), .groups = "drop") %>%